The chemical industry is taking a range of initiatives to enhance their operations within planetary boundaries. The Responsible Care® initiative and the Safe and Sustainable-by-Design concept aim to address these environmental targets from the design phase. Additional legislation like the European Regulation on Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of Chemicals (REACH), and the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) also drive the chemical sector to continuously improve on areas such as environmental pollution. Focusing on the environmental footprint by reducing emissions and addressing biodiversity contributes to achieving SDG 6 ‘Clean water and sanitation’, SDG 14 ‘Life below water’, and SDG 15 ‘Life on land’.
Contribution to the EU Green Deal
The EU Green Deal priorities include reducing air, water, and soil pollution, and ensuring the sustainability of our blue economy and fisheries sectors. The chemical industry supports these goals by minimising its environmental impact. This involves reducing emissions, managing waste responsibly, and developing chemicals and materials that support sustainable agriculture and habitat conservation. The industry is also committed to achieving zero pollution, by improving air and water quality and reducing chemical usage. This is in line with the EU’s “Towards Zero Pollution for Air, Water and Soil” initiative, which seeks to reduce pollution to levels that no longer pose harm to human health or ecosystems .
Emissions of air and water pollutants
The chemical industry invests continuously in improving its production processes. Best available techniques are implemented to optimise production and minimise emissions to the environment.
Emission of air pollutants
Since 2007, the chemical industry has significantly reduced acidifying emissions into the air, with ammonia, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur oxide emissions declining by 55%, 57%, and 80%, respectively. The implementation of measures to reduce these emissions was further triggered by Directive 2010/75/EU on industrial emissions, adopted by Member States in January 2013.
Acidifying emissions to air by the EU27 chemical industry
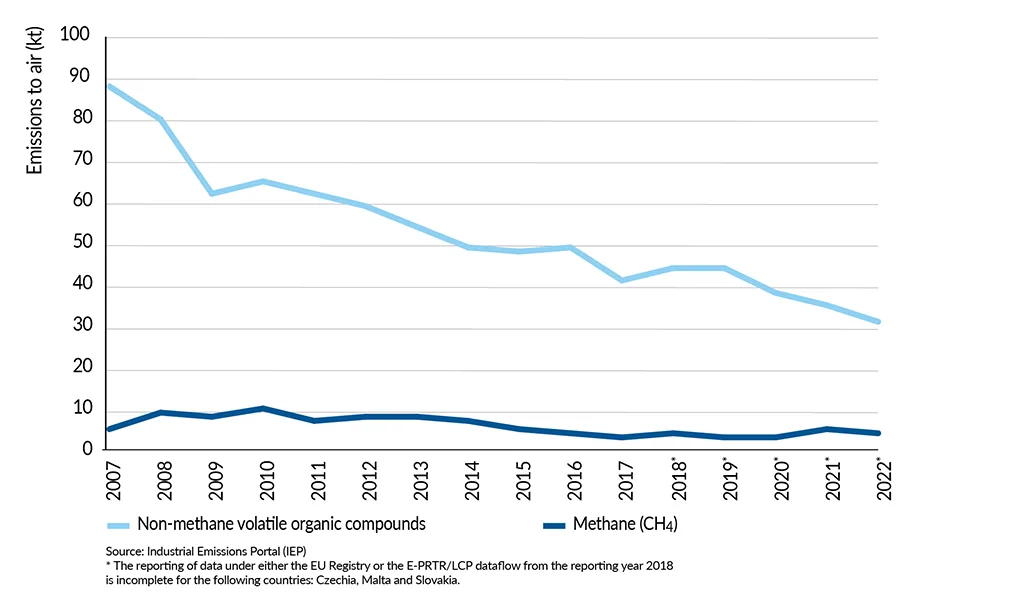
The chemical sector has achieved a 62% reduction in non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOC) since 2007 through various measures like process optimization and enhanced emissions control during storage and transport. Additionally, a declining trend in methane emissions has been observed since 2013.
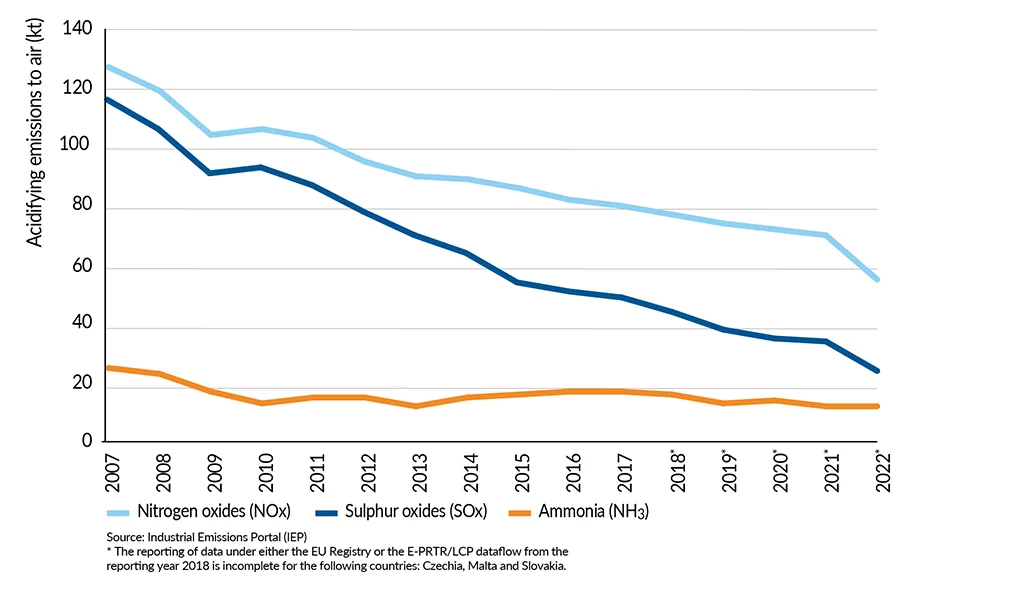
Emissions to air by the EU27 chemical industry
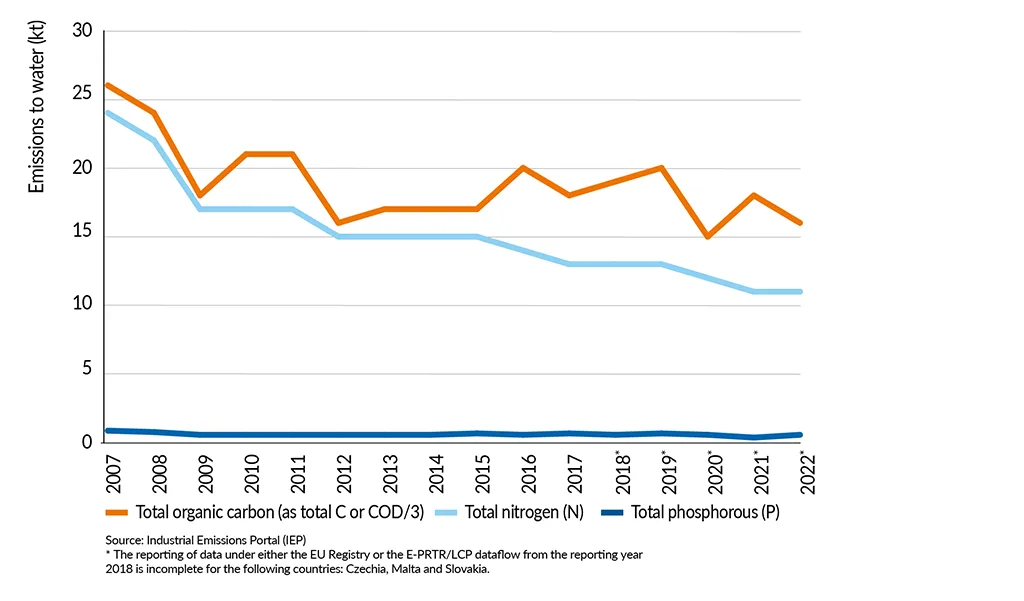
Emission of water pollutants
The Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) decreased significantly until 2012, but increased slightly again until 2019. Revisions of the Common Wastewater BREF were done in 2003 and 2016 to which companies had to comply with by 2007 and 2020.
Total nitrogen emissions have continued to decline, reaching a 57% reduction in 2021. Total phosphorous emissions show a steady trend and remain very low (approx. 0.4-0.6 kt).
Emissions to water by the EU27 chemical industry
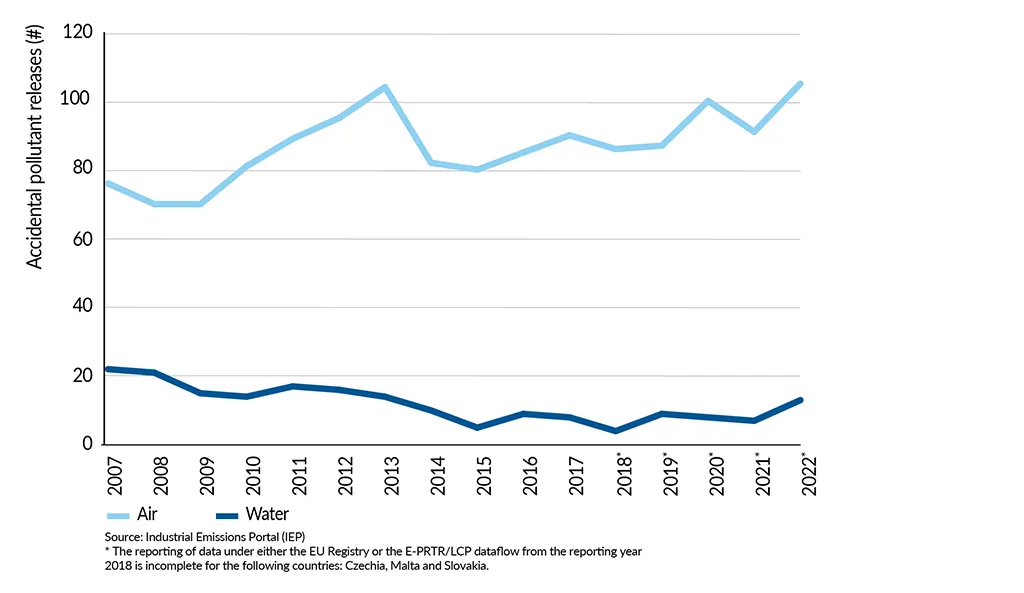
Process safety
The chemical industry strives to maximise its process safety to avoid the accidental release of chemicals to the environment. Accidental release might impact human health and the environment, and can also create unsafe working conditions.
Accidental pollutant releases
The number of accidental pollutant releases to air and water has fluctuated between 2007 and 2021, with an average of 87 releases to air and 12 to water, respectively.
Accidental emissions by the EU27 chemical industry to air and water